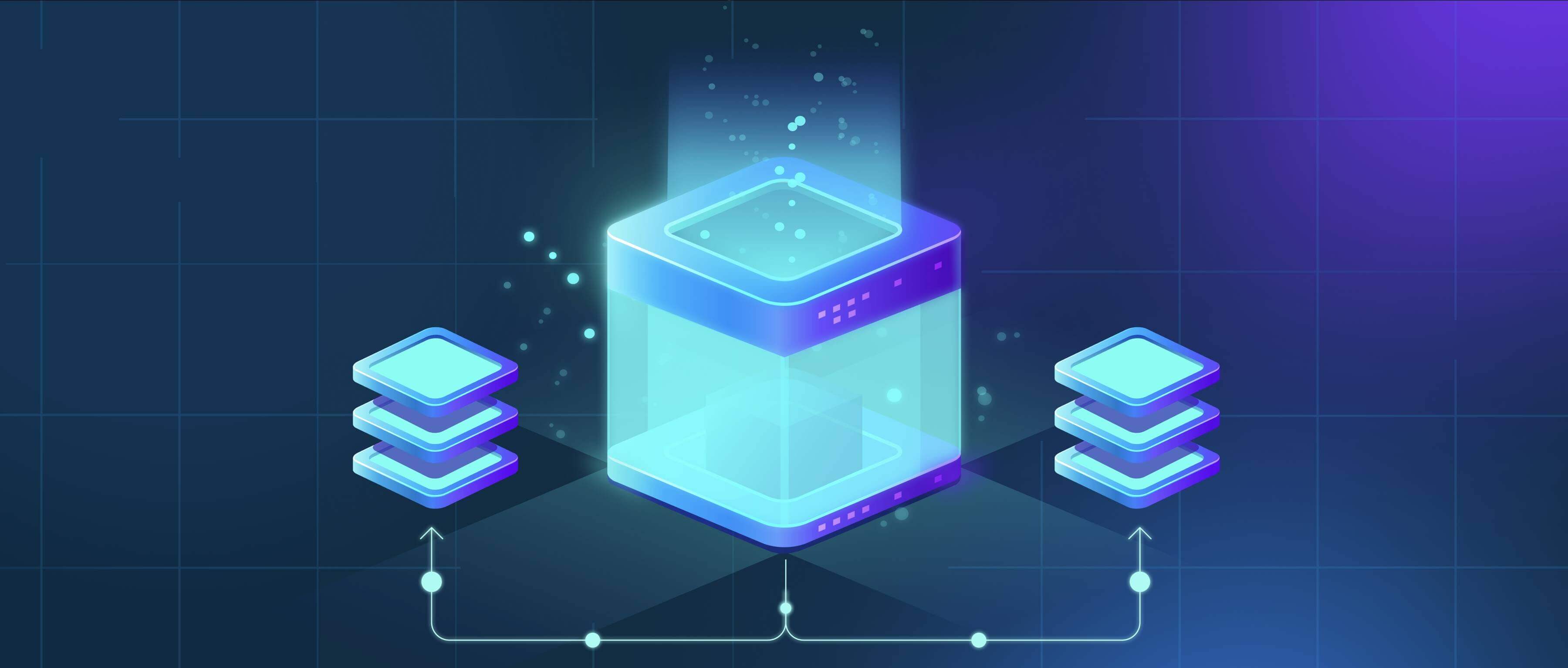
A "duplicate file found" message during an upload typically occurs because the cloud storage service or application is checking file uniqueness, not just the filename. It uses techniques like cryptographic hashing to create a unique digital fingerprint based entirely on the content of the file itself. If this fingerprint matches an existing file in your account, the system flags it as a duplicate, even if the file has a completely different name, location, or was uploaded much earlier. This prevents storing identical data multiple times, saving valuable cloud storage space.

This automatic deduplication is fundamental in cloud storage platforms (like Google Drive, Dropbox, iCloud) and backup solutions (such as Time Machine on macOS or online backup services). For example, if you try to upload the same vacation photo twice to Google Photos, even from different folders on your computer, it will detect the duplicate. Similarly, if an automatic phone camera backup tries to upload photos that already exist in your cloud library from another device, this message would appear.
The primary advantage is significant storage efficiency, reducing costs for both providers and users. A key limitation is that duplicates within the upload queue might only be detected after matching against existing cloud files, requiring the upload of unique files first. Future deduplication might involve more advanced cross-user or block-level comparison while respecting privacy. Overall, this feature promotes responsible data management but can momentarily confuse users unaware of content-based fingerprinting.
Why does my device say “duplicate file found” during upload?
A "duplicate file found" message during an upload typically occurs because the cloud storage service or application is checking file uniqueness, not just the filename. It uses techniques like cryptographic hashing to create a unique digital fingerprint based entirely on the content of the file itself. If this fingerprint matches an existing file in your account, the system flags it as a duplicate, even if the file has a completely different name, location, or was uploaded much earlier. This prevents storing identical data multiple times, saving valuable cloud storage space.

This automatic deduplication is fundamental in cloud storage platforms (like Google Drive, Dropbox, iCloud) and backup solutions (such as Time Machine on macOS or online backup services). For example, if you try to upload the same vacation photo twice to Google Photos, even from different folders on your computer, it will detect the duplicate. Similarly, if an automatic phone camera backup tries to upload photos that already exist in your cloud library from another device, this message would appear.
The primary advantage is significant storage efficiency, reducing costs for both providers and users. A key limitation is that duplicates within the upload queue might only be detected after matching against existing cloud files, requiring the upload of unique files first. Future deduplication might involve more advanced cross-user or block-level comparison while respecting privacy. Overall, this feature promotes responsible data management but can momentarily confuse users unaware of content-based fingerprinting.
Quick Article Links
How do I download and install Wisfile on my computer?
How do I download and install Wisfile on my computer? Install Wisfile directly on your computer to start organizing yo...
Which video format gives the best quality vs. size balance?
The best balance between video quality and file size is typically achieved with modern compression formats like HEVC (H....
How do I group similar files together?
Grouping similar files organizes digital items by shared characteristics, differentiating it from simply arranging files...